What is the exclusionary rule? This is one of the most pressing questions that lies within the very essence of a justice system found within the American legal framework.
The exclusionary rule is a legal rule that does not permit evidence obtained in violation of the United States Constitution to be introduced.
Current events, such as the prominent cases involving digital privacy and tracking by cell phone, are carrying this policy even further.
It is imperative for people who are concerned about civil liberties or criminal defense issues to comprehend how this rule operates.
In this article, we will elaborate on the following:
- The constitutional foundations and historical origins of the rule.
- How the rule works in daily court proceedings.
- Major exceptions that allow some evidence to remain in court.
- The global perspective on illegally obtained evidence.
The Origins And Constitutional Basis Of The Rule
What is the exclusionary rule? The exclusionary rule prevents the government from violating the law during its attempts to prove a crime. The rule is a protection for a citizen from improper practices on the part of law enforcement.
The Fourth Amendment protects individuals from unreasonable searches and seizures by the government.
Even though this right is within the Constitution, the result of a violation of the Fourth Amendment by an illegal search does not appear in the document itself. This necessitated the courts to create the tool now known as the exclusionary rule.
What is the exclusionary rule definition? It basically defines a remedy that is court-made to curb the misconduct of the police.
Historical Milestones In US Law
These early cases formed the basis for what constitutes the application of the exclusionary rule in contemporary definitions. At first, this right applied only to federal cases.
It was not until the case of Weeks v. United States in 1914 that the Supreme Court laid down rules for federal trials. Later, in Mapp v. Ohio in 1961, this rule was also applied to the states.
This meant that all police departments across America had to abide by these rules. This ensures that all enjoy protection under the Bill of Rights based on their geographical locations.
What Is The Exclusionary Rule? How The Exclusionary Rule Works In Practice
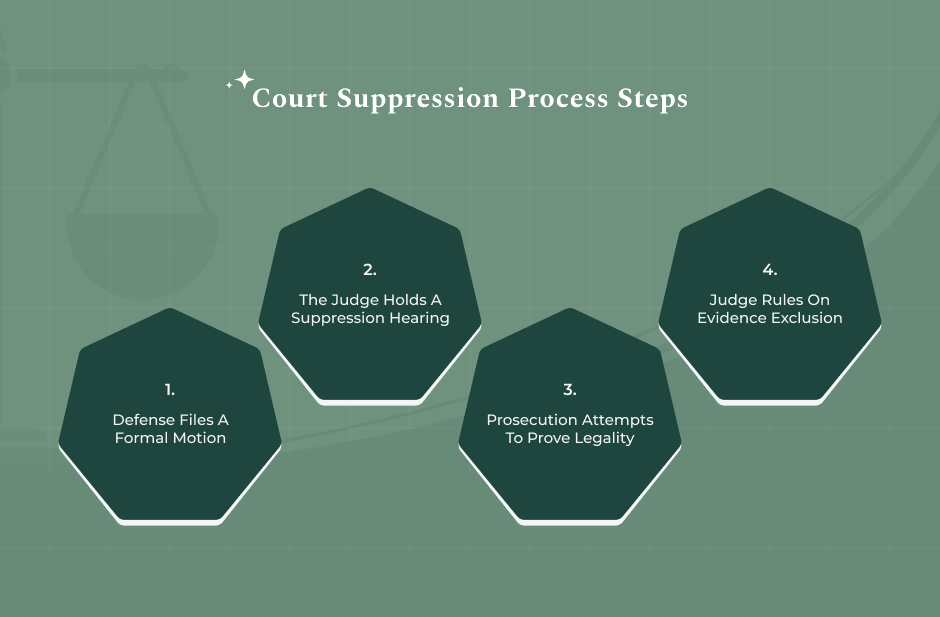
When the defendant thinks that the police are acting illegally, they have to do certain things. The journey shifts from the road to the courtroom.
The most common weapon employed by the defense lawyers is the motion to suppress evidence. This is a motion that one can file in courts that asks the judge not to submit some piece of evidence before the jury. For the motion to be successful, the defendant has to demonstrate how his or her rights have been violated during the search.
The Court will deem this “inadmissible.” Charges have often been dropped when the principal proof of the crime is ruled “inadmissible.”
The Fruit Of The Poisonous Tree
This colorful legal phrase refers to evidence that you obtain as a result of a prima facie illegal act. It does stretch the exclusionary rule.
Furthermore, if the primary search is illegal (the poisonous tree), then the evidence from this illegal search is likewise illegal (the fruit).
For instance, if the police break into a house illegally and retrieve a map that gives directions to a hidden stash of drugs, this stash will become inadmissible. This ensures that the police cannot use the illegal search for self-proving purposes.
Major Exceptions And Limitations To The Rule
However, not all illegal searches lead to the suppression of evidence, as a balance of rights and public safety is maintained under the law. Several exemptions have been developed in this regard.
What Is The Exclusionary Rule Without Its Exceptions?

This would be an even tougher standard for prosecutors. The most significant of these carve-out exceptions would be the good-faith exception, as per the Legal Information Institute.
When the police assert a valid search warrant in good faith, but it later proves invalid on a technicality, the evidence may be admitted.
The courts feel that it does not make a statement about deterrence if an officer gets caught up in a judge’s technicality.
Other Paths To Admissibility
Often, evidence is admitted if the link between the evidence and the unlawful act is very tenuous. Such doctrines prevent the rule from being overbroad.
The independent source rule allows admission of the evidence if it was discovered as a result of an independent legal source.
In addition, in cases where it is proved that the police would inevitably have discovered the evidence using legal means, it is governed by the inevitable discovery rule.
This rule aims to ensure that the exclusion of the evidence does not place the police in a worse position than before.
What Is The Exclusionary Rule? Key US Supreme Court Cases To Know
Some illustrious courtroom cases have presented the definition of the exclusionary rule over the past hundred years. These cases illustrate how the rule expanded and was subsequently narrowed.
United States vs. Leon
United States vs. Leon in 1984 marked another significant point in the development of the good-faith exception. This case indicated that the court started paying more attention to the fact that persons who commit crimes may go free because of technicalities.
Much later, in Davis vs. United States in 2011, the court ruled that evidence cannot be suppressed as long as the police are acting in compliance with the law as it is at that time.
All these incidents influenced the perception of what constitutes the exclusionary rule among lawyers and law enforcement personnel. They contain the playbook for the modern trial.
Arizona v. Evans
In the case of Arizona v. Evans, it was held that the evidence was allowable despite the fact that it was based on an error that appeared in the computer database of the courts.
This further supports the assertion that the rule’s application is only meant to deter the problem of police misconduct and not errors that occur in the courts.
Comparative And Global Perspectives

In regard to illegally obtained evidence, the United States is uniquely rigid in its exclusion. In other countries, there is more latitude for this question.
However, in the UK, the courts have the discretion to exclude the evidence if it would render the trial unfair. They do not have the same rigid rules governing the issue in the US.
In Canada, the courts consider whether the error would bring the administration of justice into disrepute. This enables the courts to judge the level of police misconduct and the offense.
What Is The Exclusionary Rule? – The Exclusionary Rule In India
The Indian legal system approaches such questions in a manner that differs significantly from American courts. In general, it gives more weight to the search for the truth than to the means of obtaining it.
In India, evidence may be admitted even if it was gathered during an illegal search. This is due to relevance.
Although there are some safeguards in place regarding these matters, these safeguards are not as strict as those in US law regarding the standards of the exclusionary rule.
This comparison of law illustrates how the exclusionary rule is essentially an American phenomenon to control police powers.
Practical Implications For The Legal Team

What is the exclusionary rule? This rule affects the manner in which the prosecution and defense prepare for a criminal trial. It makes the police and lawyers very cautious with how they do things.
For defense attorneys, it is a high-ranking concern to identify a violation of the Fourth Amendment. They have to examine all the circumstances under which evidence was gathered.
For prosecutors, the exclusionary rule dictates that before even crafting their case, it is their responsibility to check the legitimacy of each search. If not, their case could fall apart at the very end.
Impact On Law Enforcement Training
Police forces are required to continually train to be abreast of court decisions. One erroneous step in a search warrant can jeopardize years of work.
Police officers are taught to err on the side of caution and to get a warrant whenever it is possible. They also learn to document their “good faith” to avoid a motion to suppress their evidence.
This demonstrates the deterrent effect of the exclusionary rule to be a reality, as it affects the way police officers act on the street.
Criticisms And Future Trends

What is the exclusionary rule? What is the relevance of the current applicability of the exclusionary rule to our rights? It has been considered too expensive for society.
One of the criticisms of the rule is that it allows criminals to go free as a result of small police errors, according to the Office of Justice Programs.
There are those who advocate that we should employ other techniques, such as suing police officers, rather than just suppressing evidence.
On the other hand, some individuals believe that if the rule were abolished, then the Fourth Amendment would actually become meaningless. With advancements in terms of AI, issues about the future of the rule are paramount.
Technology And Digital Privacy
Contemporary searches are often conducted on servers or within the cloud. This gives rise to difficulties for the rule.
What is the exclusionary rule? How the exclusionary rule applies to geofence warrants and data mining is now before the courts. When the government starts obtaining a warrant for each individual in a particular geographic region, is that unconstitutional? Digital searches are going to be the next big fight related to the suppression of evidence. It is going to become outdated soon because it is now a high-tech world.
Read Also: Countries With No Extradition Treaty With The United States
Expert Tips For Compliance And Protection
Lawyers and civilians can do what it takes to make the legal system function for its intended good. Protection begins with familiarizing oneself with the rules.
For investigators, it is always important to record what is termed an “independent source” if one has any reservations about search validity. Defense attorneys should always file a motion to suppress as early as possible to serve as evidence in an appeal. Citizens must be aware that should they “consent” to a search, they will not qualify for the exclusionary rule.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
The Exclusionary Rule has been an area rich in complexities, which often results in numerous questions about how justice could be delivered in this context. Here, we will answer a few queries related to this rule.
The exclusionary rule only applies to the actions of governmental agencies such as the police. If your neighbor breaks into your apartment and discovers some illegal goods, he can hand them over to the police, and such evidence will be admissible. The exclusionary rule only regulates governmental behavior.
Ordinarily, the rule applies only in criminal trials. In most civil matters, the court wants as much evidence as possible to determine the merits between two private parties. Although there are some extremely narrow exceptions for civil forfeiture, the exclusionary rule indicates that its home base is in the criminal justice process.
If the judge erred and admitted improper evidence, the defendant might appeal the conviction. If the appellate court determines that the evidence should have been excluded, it might reverse the verdict. This serves as a second check to properly define the standards for exclusionary rule cases.
If you feel that your rights have been violated in any form or manner during a police search, it is best to immediately contact a competent criminal defense attorney to discuss the possibility of a motion to suppress.

















