It’s a common fact in the Legal world that not naming a Contingent beneficiary can plunge your financial wishes for the future into utter chaos. Now, if you want to ask “What is a Contingent Beneficiary?”, we have the answer. Knowing the contingent beneficiary meaning is a key decision for anyone with assets.
This article explains what a contingent beneficiary is, how they work as a vital fall-back. We also talk about how you can make sure your assets go to the person you want.
What Is A Contingent Beneficiary? Definition, Rules & Best Practices
When you establish an insurance policy, a retirement account, or a Will, you name people to take your property when you die. First you name a primary beneficiary: the person who has the first right to the funds or property.
A contingent beneficiary is your important alternate choice. This beneficiary works as financial protection for you, receiving the assets only in case the primary beneficiary cannot, for one reason or another. Thus, in simple words, what is a contingent beneficiary? They are an alternate recipient.
The whole thing hinges on an event called a contingency that must occur. You need to fully comprehend that what is a contingent beneficiary essentially describes them as a secondary beneficiary. They only inherit if the primary option is eliminated from consideration altogether. They offer a simple, powerful layer of certainty in your estate planning.
Definition & Core Concept
What is a contingent beneficiary? Well, a contingency beneficiary is the alternative, or secondary, recipient of property. The contingent beneficiary receives the inheritance only upon the occurrence of certain events, specifically the failure of the primary beneficiary.
The contingent beneficiary designation in legal and financial matters, such as life insurance policies, retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s, and Transfer-on-Death accounts, keeps the assets out of probate.
Contingent beneficiaries, according to financial institutions like Investopedia, are those who receive benefits if all the named primary beneficiaries die, decline to accept the assets (disclaim), or are otherwise legally unable to receive the funds.
Primary Vs Contingent Beneficiary- How It Works
The hierarchy of recipients is important to comprehend.
Primary Beneficiary
This is the first person or group you name to get the assets. They inherit automatically on your death. They must be alive and capable of accepting the inheritance.
Contingent Beneficiary
So, what really is a contingent beneficiary? This is your alternate selection. The contingent beneficiary only inherits in place of the primary when the primary cannot inherit.
That dual structure is why naming a contingent beneficiary is fundamental to responsible estate planning. In addition, estate planners sometimes refer to an “alternate beneficiary” or “secondary beneficiary.”
These generally carry the same meaning as contingent beneficiary. Sometimes, though, particularly with regard to trusts, another term is used: “remainder beneficiary.” Those are the recipients when the trust terminates, which is related but not precisely the same concept.
Why You Should Name A Contingent Beneficiary?
Most Americans are really focused on naming their primary beneficiary, and then they just forget that second step; that’s where the gap in planning comes in for them. Naming a contingent beneficiary is not optional. It’s a must for risk mitigation.
Preventing Assets From Entering Probate
What is a Contingent Beneficiary? Why should you have one? The major reason a person will name a contingent beneficiary is to avoid the costly, time-consuming process of probate.
Consequences Of Not Naming A Contingent Beneficiary
If you don’t name a contingent beneficiary and your primary beneficiary dies before you do, the assets will usually revert to your general estate. The assets must then be distributed in accordance with the terms of your Will, if you have one, or according to state intestacy laws if you don’t. This process is called probate.
Probate can keep money and property tied up for months and even years and involves quite significant legal fees too. Naming a contingent beneficiary entirely avoids this because the assets will pass directly to the named party at your death. NerdWallet emphasizes that this action will protect your intent and carry it out in an efficient manner.
Making Your Intentions Clear And Avoiding Ambiguity
Nobody wants their last will and testament to potentially create family disputes. You are taking away any ambiguity as to who should get the assets, by naming a contingent beneficiary, in case your first choice defaults. This prevents any disputes between relatives or creditors. Ultimately, what is a contingent beneficiary and the reason to have one is primarily to have peace of mind.
What Does Contingent Beneficiary Mean? How Contingent Beneficiaries Work
What is a contingent beneficiary is mainly answered by what they do. The action of a contingent beneficiary is not complicated but rather straightforward. What is a contingent beneficiary and what are some benefits of having one? Well, once the primary condition has been satisfied, the contingent party will get nothing.
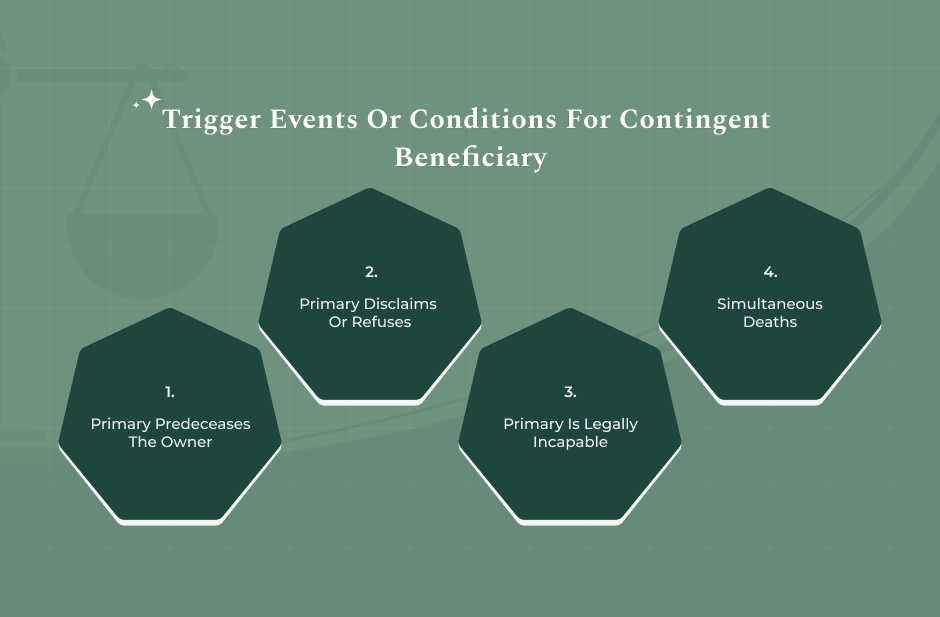
A contingent beneficiary receives the assets only upon the occurrence of any one of the following key trigger events:
Primary Predeceases The Owner
This is the most common scenario. If the primary beneficiary dies before you do, the benefits are immediately passed to the contingent beneficiary.
Primary Disclaims Or Refuses
The primary beneficiary legally has the right to disclaim an inheritance. If they do so, the funds pass to the contingent beneficiary.
Primary Is Not Locatable Or Legally Incapable
The funds transfer to the contingent beneficiary in the unlikely event of the principal beneficiary being unavailable or, by operation of law, incapable of accepting the inheritance, such as being adjudged.
Simultaneous Deaths
This is a critical, high-risk scenario. Many states follow the Uniform Simultaneous Death Act if you and the primary beneficiary die at the same time, or within an extremely short period. It considers the primary to have predeceased you.
Thus, this triggered the right of the contingent beneficiary to inherit the assets with immediate effect [Insuranceopedia].
What Is A Contingent Beneficiary- Allocation And Multiple Contingent Beneficiaries
You can name multiple contingent beneficiaries and specify a certain percentage of the assets for each.
For example, you might name your sister and your favorite charity as contingent beneficiaries, each to get 50%. If one of those two contingent beneficiaries also cannot inherit, that portion of the assets normally goes to the remaining named contingent beneficiaries or else back to your estate.
The Importance Of Per Stirpes
When you name a group of contingent beneficiaries, you will often see the term “per stirpes.” That’s Latin for “by roots.”
If you name your children as contingent beneficiaries per stirpes and one of your children dies before you, that child’s share automatically passes to that child’s own children (your grandchildren). If you don’t use “per stirpes,” the deceased child’s share usually falls to the remaining named contingent beneficiaries in one form or another. This is one of those items that many people misunderstand, so make sure you word it correctly.
Contingent Beneficiary In Specific Contexts
What is a contingent beneficiary and what is the importance of it in different scenarios? It’s a little different depending on account and asset type.
Life Insurance Policies
The most common asset associated with the designation of a contingent beneficiary is life insurance. Life insurance companies like Aflac focus on this designation. Upon the death of the primary recipient, the death benefit goes directly to the named contingent beneficiary.
What If No Contingent Is Named?
If both the primary and contingent beneficiary predecease you, the proceeds are paid to your estate. This subjects the funds to probate and creditor claims.
Retirement Accounts (IRAs And 401(k)s)
It is legally important that you name a contingent beneficiary of retirement accounts because of the various rules controlling tax-advantaged savings. The SECURE Act changed the distribution rules for inherited IRAs in 2019. This law generally requires non-spouse beneficiaries to drain the account within ten years of the original owner’s death.
By naming a contingent beneficiary, you identify who receives these assets and, consequently, who has to satisfy the complicated tax distribution requirements. If the contingent beneficiary is a spouse, they are often able to roll the funds into their own IRA to take advantage of more favorable tax treatment.
Wills, Trusts, And Estate Planning
In a Will or a Trust, what is a Contingent Beneficiary? Well, the contingent beneficiary is often named as the final “remainder beneficiary.”
Will
A Will might declare your spouse as the main beneficiary of your estate, followed by naming your children as the contingent beneficiaries.
Trust
A trust document contains similar language that dictates what happens with the assets in case of the failure of the first beneficiaries.
It is essential that your Will or Trust documents match the beneficiary designations on your bank accounts and insurance forms. Conflicting designations give rise to legal disputes.
What Is A Contingent Beneficiary Jurisdiction- Legal Shades
To understand what a contingent beneficiary is, one also needs to consider specific state and country laws. Most of these are crafted in order to elucidate the exact moment of inheritance.
U.S. State Variation and Doctrine
In the U.S., most states adhere to the Uniform Simultaneous Death Act. This statute establishes the survival requirement, usually 120 hours-five days. Therefore, if a primary beneficiary dies within less than 120 hours after you, then by definition, he or she pre-deceased you, which immediately triggers the inheritance by the contingent beneficiary.
The Slayer Rule
This legal doctrine, which is imposed by state statute, stops a person who unlawfully kills you from inheriting your assets. If the primary beneficiary is prevented by the Slayer Rule, the assets directly pass to the contingent beneficiary [Legal Information Institute].
International Perspective
While the terminology may be different, the definition of a contingent beneficiary is universal.
India
Similar to a primary beneficiary, Indian law provides for “Nomination.” This may or may not override a Will in the case of life insurance/investments.
Very often, a secondary nominee is used to ensure quick transfer, though the ultimate legal heir as determined by the Will or succession law might eventually control the asset. You must check the specific financial instrument rules.
United Kingdom
Assets held in Trust or insurance “written in trust” which names beneficiaries outside of the Will serve similarly to contingent beneficiary designations to avoid probate in the UK.
Risks, Pitfalls & Edge Cases
The biggest risk, of course, is not naming a contingent beneficiary. But even when you do fill out the form, mistakes can be made.
Primary and Contingent Both Die If both your primary and contingent beneficiary die before you, or in quick succession, the assets revert to your estate. You should always name a “tertiary” or “final” contingent beneficiary-perhaps a charity or a trust-to prevent this.
Ambiguous Language
Using general terms, such as “my family, or not specifying per stirpes can be the source of potential litigation. Use full legal names and be specific about the percentage distribution.
Obsolete designations
Major life events that could happen in one’s life include divorce, remarriage, and the birth of children. Failure to change these forms means that an ex-spouse can inherit – despite your intentions – because they remain the named contingent beneficiary on an old form.
Read Also: Understanding Common Law Marriage: Legal Recognition Without Ceremony
Best Practices & Expert Tips Pertaining To What Is A Contingent Beneficiary

The following are the steps you should take to ensure that your contingent beneficiary designations are legally valid.
1. Review And Update Regularly
Review your insurance, 401(k), IRA, and TOD account beneficiary designations after you get married, divorced, or become a parent.
2. Use Clear Legal Names
Always record a full legal name, date of birth, and Social Security Number (when available) for all contingent beneficiaries. Never use nicknames.
3. Documentation Management
Ensure that the beneficiary language in your Will or Trust exactly matches the forms on file with your financial institutions. Mismatches are an open invitation for a court battle.
4. Know Your Terms
Understand the difference in naming contingent beneficiaries “per stirpes” and “per capita.” Choose one that best reflects how descendants are to receive assets.
Knowing what is meant by the term contingent beneficiary, and following these steps, you basically build a fortress around your financial legacy.
What Is A Contingent Beneficiary – Frequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts on what separates a seamless legacy transfer from an extremely costly legal mess is the understanding of what a contingent beneficiary is. Know who your named contingent beneficiary is on every major asset today. Set up regular reviews to ensure your wishes are carried out.
If you leave the contingent beneficiary designation blank, then the proceeds of your IRA become payable to your estate.
This is a serious problem: first of all, the assets will be in probate; even worse, distribution may be according to state law and not specifically according to your wishes. Moreover, the IRA will lose the protected status that it enjoyed and may be subjected to more burdensome or rapid taxation than if it had been inherited by a named individual.
In this frequently occurring, unfortunate scenario, the contingent beneficiary, your children, will instantly receive the policy proceeds. Applicable state law, such as the Uniform Simultaneous Death Act, will presume that your spouse (the primary) predeceased you.
This “failure” of the primary then triggers the right of the children to the money as contingent beneficiaries. This process completely avoids probate.
Yes. You can name a minor child as your contingent beneficiary. However, a minor cannot legally manage inherited money. The general rule is that the court will appoint a guardian to manage the funds until the child attains the age of majority, generally either 18 or 21.
Or you can just appoint a contingent beneficiary.
You would then provide the rules of the trust in your Will, which would ensure a trustee manages the funds for the benefit of the child in accordance with the wishes you supply.

















