In common law-based judiciary, the decisions of the courts in the past have a very significant influence on how cases will be decided in the future. The principle that names one of the main pillars of the whole legal system – the precedent – is the primary source of legal predictability and uniformity.
Out of all kinds of precedents, a binding precedent is the most powerful because the courts of the lower level have to abide by it.
Binding precedents are the sources of influence not only on the judges and the lawyers but also on the ordinary people as they determine the decisions in various fields such as civil rights, criminal law, consumer protection, and constitutional freedoms.
In this article, I will talk about the following things:
- What is a binding precedent?
- What are the types of binding precedents?
- Key elements of binding precedent.
- How does it work?
- The legal impact of a binding precedent.
Additionally, I will also talk about some of the questions that people often ask about this topic. Therefore, if these are some of the questions that you want to know, keep on reading this article till the end…
What Is Binding Precedent?
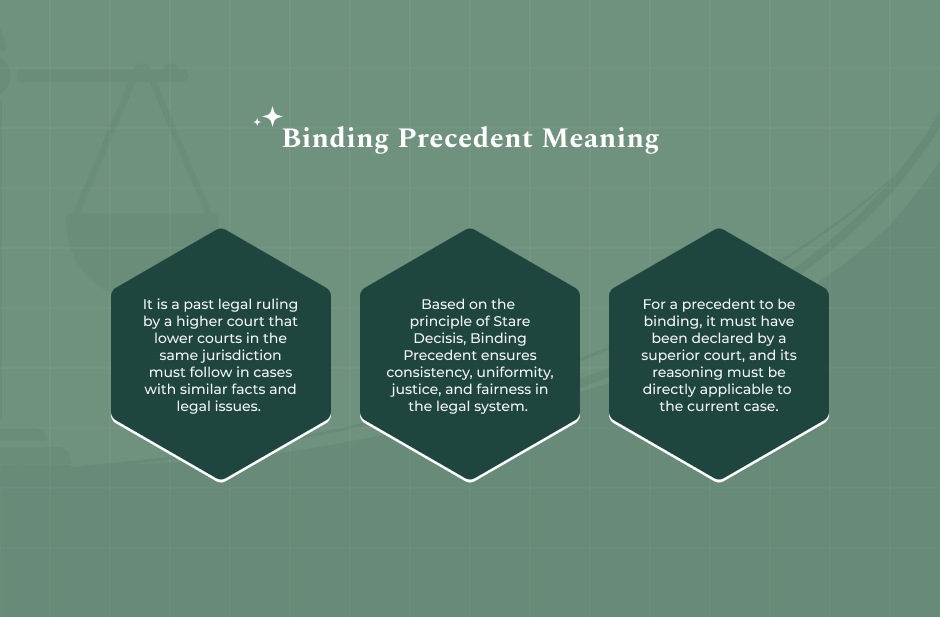
A binding precedent is a previous court ruling that must be followed by courts when deciding a case with similar facts or legal issues. It ensures consistency in judicial decision-making and is part of the doctrine of stare decisis (Latin for “to stand by things decided”).
“Binding precedent is a legal rule or principle, articulated by an appellate court, that must be followed by lower courts within its jurisdiction,” states Legal Information Institute.
In the United States, rulings of the U.S. Supreme Court bind all federal and state courts. According to LII, the term precedent is “a court decision that is considered an authority for deciding subsequent cases involving identical or similar facts, or similar legal issues.”
To a great extent, the appellate court’s decision will be presented in the form of a written opinion. Such a written opinion will clearly outline the legal issue and the court’s determination regarding it.
The determination, called a holding, is the one that has legal effect for all the lower courts that are in the same jurisdiction, i.e., they are obliged to give the same solution if they come across similar facts in accordance with the court’s decision.
Therefore, the lower courts are bound, or in other words, they have to follow the legal precedent that the higher court has set. This system helps avoid arbitrary judgments and maintains stability in the law.
What Are The Types Of Binding Precedents?
Binding precedents operate differently depending on their scope. Here are some of the different types that you need to know about:
| Type | Meaning |
| Vertical Binding Precedent | Lower courts must follow decisions of higher courts within the same hierarchy. |
| Horizontal Binding Precedent | Courts adhere to their own past decisions unless there is a strong justification to overturn them. |
| Constitutional Precedents | Court decisions interpreting the Constitution are binding until overturned or amended. |
| Statutory Precedents | Judicial interpretations of legislation may be overridden by legislative amendments. |
What Are The Key Aspects Of A Binding Precedent?
Not every part of a judicial decision is binding. Courts analyze specific components. These are basically the key aspects of the principle of binding precedent. Here are the key elements or aspects that you need to know about:
- Ratio Decidendi (Reason for the Decision): The legal principle that is binding coming from a court decision. The example of such a case is Donoghue v. Stevenson [1932], the court that created the concept of the duty of care in negligence.
- Obiter Dicta (Things Said by the Way): Judges comments made in passing or hypothetical situations given. Non-binding, but may have a persuasive effect.
- Judicial Hierarchy: Only those precedents from a court of higher authority within the same jurisdiction that are binding.
- Jurisdictional Limits: A precedent from the UK is not binding in the U.S. but may be persuasive.
How Does A Binding Precedent Happen?
A binding precedent is when the higher court decides a new principle of law (the ratio decidendi) in a previous case that the lower courts in the same jurisdiction have to adhere to, an idea referred to as stare decisis (“to rely on decided matters”). As a result, the decisions of the U.S. Supreme Court are binding on all federal as well as state courts.
A binding precedent arises only under specific conditions. Here’s how it happens:
- New Legal Principle Established: Courts create a new rule when existing law is unclear.
- From a Higher Court: The precedent originates in a superior court.
- Ratio Decidendi Clearly Stated: The principle of law is clearly articulated.
- Accessible Judgment: Published in official law reports.
Examples:
• U.S.: Miranda v. Arizona (1966) established Miranda rights, binding police nationwide.
• India: Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala (1973) established the basic structure doctrine in constitutional law.
• UK: R v. R (1991) set a precedent by criminalizing marital rape.
What Are The Legal Impact Of A Binding Precedent?
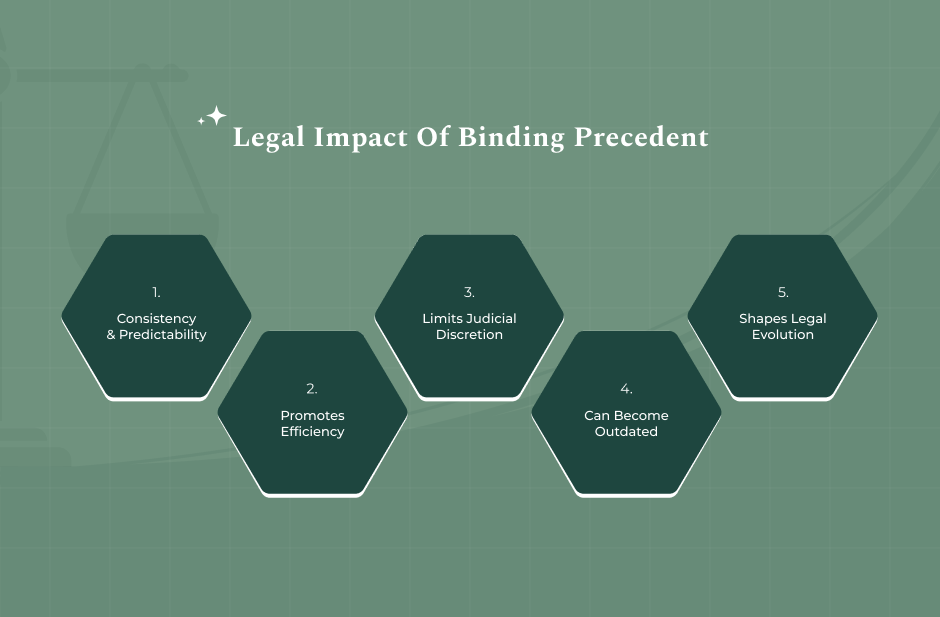
The consequences or the legal impact of binding precedent can be far-reaching. Here’s how it impacts society and shapes law:
Consistency And Predictability
Binding precedents largely guarantee that similar cases are treated in the same manner, and as such, they avoid the occurrence of arbitrary decisions and also give an idea of how the law is going to be applied in different cases in the future.
Efficiency And Certainty
Through the use of past decisions, courts can handle new cases in a shorter time, and legal entities can have a better judgment of the outcome of a case depending on the established legal principles.
Stability Of The Law
The concept of stare decisis (“to stand by things decided”) is a mechanism that contributes to the stability of the legal rules by limiting the number of changes; though occasionally, higher courts might be able to reverse their own precedents if the situation is very compelling.
Hierarchical Structure
The use of precedents goes in favor of the court system hierarchy as the decisions of higher appellate courts are binding on all lower courts within their jurisdiction and therefore those courts must follow them.
Fairness
Binding precedent is one of the factors that make the legal system fair as it enforces judging standards and also makes sure that similar facts of the case will lead to similar legal consequences.
Read Also: What Is A Bench Trial: Legal Definition & Meaning
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Now that you are aware of what a binding precedent is, let me tell you some of the most common questions that people also ask when it comes to this legal term. Therefore, take a look at them before you leave:
A binding precedent is a court decision in the past that a lower court in the same area must follow by law. A persuasive precedent, on the other hand, is a previous decision that a court can look at but is not required to follow.
Not really. A precedent is refered as an indication of what the law means. Although binding precedents play the role of law in later cases, they are still able to be changed by the decisions of higher courts or through legislation.
Definitely, but only in cases involving statutes. Changes to the constitution are usually necessary for constitutional precedents to be modified.
In the first place, their rights in the areas of criminal trials, employment disputes, property cases, and constitutional freedoms are the ones that are most affected by them.